Application Security in .NET Framework: Web, Mobile, Cloud

In 2020, Wattpad, a user-generated stories platform, suffered a massive security breach. Email addresses, dates of birth, IP addresses, and other data of 268 million users were exposed and sold online.
Wattpad’s case is just a droplet in the ocean though. Overall, 2935 publicly reported breaches occurred in the first 9 months of 2020.
Such a vulnerable state of software isn’t surprising. Mobile and web application security is a complex process that starts with requirements analysis and ends with a user’s knowledge of security practices. It encompasses the entire development lifecycle, and any misstep along the way can leave behind a weakness.
But app security depends not only on the mastery of software developers but on the vulnerability of preferred development platforms. In this article, we’ll take a look at the latter to answer how secure is Microsoft’s .NET? But first, let’s find out what the greatest cybersecurity risks are.
The Most Common Types of Security Breaches
There are hundreds of ways your software might get breached, hacked, or muddled with. But, a few of the most popular persist through time. They include the following types of security breaches:
- Malware attacks. Viruses, file infectors, trojans, logic bombs, ransomware, and the rest of software the purpose of which is to meddle with your system.
- Distributed-denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. A server gets spammed with requests until it fails.
- Password guessing. An embarrassing number of people continue using simple passwords, which can be guessed to gain access to the system.

- Phishing attacks. Getting important information, such as passwords, logins, banking data, from users by the means of psychological manipulation or fraud.
- Cross-site (XXS) attacks. Injecting malicious scripts into websites and apps.
- Cross-site request forgery (CSRF) attacks. Performing actions via user’s accounts by exploiting HTTP requests.
- SQL injection attacks. Sending an SQL request under the guise of a usual user request, which then is unwillingly executed by the system.
- Open redirect attacks. Meddling with badly-constructed URLs to redirect users to another destination.
- Man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM). It comes in many forms, but, in essence, MITM is digital eavesdropping.
As you see, a part of security breaches is “people problems.” They are the result of either inattentiveness, recklessness, or lack of knowledge on the topic. The rest can be addressed by software developers and the framework itself.
Security in .NET
The major advantage of .NET is that the platform is under Microsoft’s responsibility. As the biggest software company that reigns over the most popular OS in the world, Microsoft can’t afford a vulnerable development platform.
Very few, if any, platforms can brag with such a professional security overseer. For example, Java is an open-source platform. That means that often enthusiasts and interested parties keep it up to date.
Security in .NET is one of Microsoft’s top priorities. The company works to prevent any major security breaches as soon as a new vulnerability is discovered.
Besides, the tech giant targets web and mobile application security threats on several different levels by using a “combination of technology, operations, legal action and policy to disrupt and deter malicious activity.”

Security in .NET itself has many pivots, of which we want to emphasize three: code access security, encryption, and verification.
CAS is a special security feature that protects the .NET framework from unauthorized access to its operations and data. CAS comes into play every time a third-party code tries to gain access. The mechanism checks whether the code has the right through the evidence of assembly, which checks the source of the code. As a result, any malicious software will have a much harder time pretending to have access to interfere with the .NET performance.
Cryptography. For better security in dot NET, it has an in-built set of cryptographic features and algorithms. They are easy to use and help ensure high application security.
Verification. It’s a final step of managing executed code that significantly mitigates the risk of any unexpected operations that can otherwise ignore other security measures. As a result, verification helps to prevent a huge swath of possible security vulnerabilities, which can easily “slip” into the software.
Of course, security in dot NET is much more than that. But, the provided information gives a nice idea of where the platform’s protection standards stand.


.NET Software Development
Microsoft Gold Partner with 16 years of experience.
Now, let’s take a closer look at other frameworks within the bigger .NET ecosystem: ASP.NET, Azure, and Xamarin.
ASP.NET Security vs ASP.NET Core Security
Yes, ASP.NET and ASP.NET Core are two different things.
ASP.NET is an open-source framework for web development.
ASP.NET Core is a faster, better, and more secure cross-platform web framework. When it comes to web application security, ASP.NET security has a few substantial benefits:
1. Core’s predecessor has been a solid framework with a strong legacy. Developed in 2002, the original ASP.NET evolved along with the more sophisticated hacker attacks and security breaches. If the framework didn’t stay up to date, it would’ve faded into obscurity. It lasted for 17 years and eventually got “reborn” as ASP.NET Core.
2. Includes tools for managing and storing valuable data without exposing it in the app’s code.
3. Microsoft provides techniques for .NET Core protection against most common web vulnerabilities, such as:
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) attacks
- SQL injection attacks
- Cross-Site Request Forgery (XSRF/CSRF) attacks
- Open redirect attacks
- DDoS attacks
ASP.NET Core security is up to the standards. The framework provides a flexible set of tools and technologies for building well-protected web applications.
ASP.NET MVC vs ASP.NET Core
Why Use It for Web Development?
Azure Security
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing service that includes SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS.
Azure cloud security consists of three elements:
- Physical security, which is basically how well the server infrastructure is protected
- Infrastructure security, which is monitoring infrastructure to detect any abnormalities and patch up any arising issues.
- Data and access security, which is the security of data encryption, transmission, and management.
As one of the top 3 cloud service providers, Microsoft Azure scores high in the first two departments no doubt. The third though isn’t completely under Microsoft’s responsibility. It’s up to customers’ developers to ensure proper adjustment, implementation, and management of data encryption algorithms and access privileges.
Among Azure cloud security features is the Azure Active Directory (Azure AD). It’s an enterprise identity service for managing all authorizations and permissions from a single place.
Also, Azure has an Azure Security Center, which is “security posture management and threat protection for your hybrid cloud workloads.”
With it, you can
- Monitor and manage the security state of the entire infrastructure, including servers, storage, SQL, networks, applications, and workloads that are running in Azure, on-premises, and in other clouds;
- Check compliances with regulations;
- Investigate security threats;
- Integrate third-party security solutions.
Besides, ASC comes equipped with Azure Defender, which further enhances the Azure cloud security.
On the downside, Azure has comparably lacking documentation as well as a habit to default to a basic state on new instances of virtual networks, which requires manual adjustment. Also, the functionality that is available to you changes depending on the chosen price option. As always, more money = more features and flexibility. But, that’s true for all cloud computing services.
Microsoft Azure requires some tinkering to ensure that its digital fortifications are up and charged. So, if you decide to go with Microsoft Azure, it’s better to hire people who know how to deal with it. Just like its direct competitors — AWS and Google cloud — when managed well, Azure is among the most secure cloud computing platforms in the world.
Abto Software proved its competency in Cloud Platform
To gain silver status in the area, our teams received four Azure certifications.
Xamarin Security
Xamarin is a framework for native iOS, Android, and Windows mobile development.
The framework has almost everything required for mobile application security. The only downside to Xamarin security is that Xamarin-compiled Android apps are vulnerable to reverse-engineering attempts. To minimize the risks developers can use obfuscators to “muddle the waters” for any person who’ll try to look under the hoof of the app.
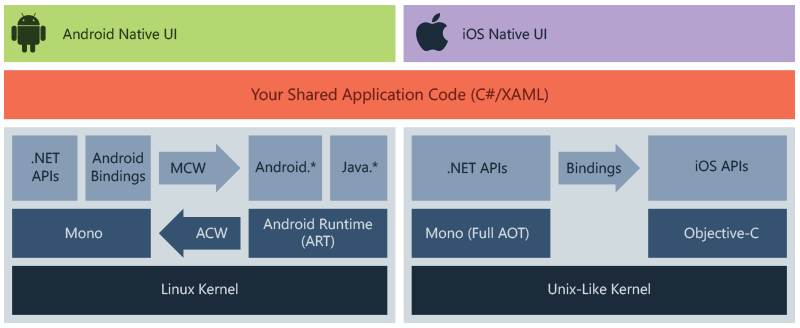
The mobile application security comes down to how developers use the tool. If they use secure storage, encrypt data, and write robust code, you have nothing to worry about.
Xamarin is young compared to its older sibling ASP.NET. Besides, it isn’t an internal product of Microsoft. So, it doesn’t have that same solid base and rich legacy that other parts of the .NET ecosystem may have.
However, Xamarin is among the leaders of mobile development frameworks. For example, the World Bank, Alaskan Airlines, UPS, and the Academy of Motion Pictures Arts and Sciences are among the organizations that chose Xamarin for its mobile projects. If you want a secure mobile app, Xamarin is a good choice.
Summing Up
Perfectly protected software doesn’t exist. At the end of the day, any application is as secure as the least experienced developer in the team is skilled in their craft. But, the better the tool in their hands, the fewer chances random security vulnerabilities will occur.
.NET has all the essentials a developer can use to create a well-secured application. No wonder, the platform remains among the most popular choices for the development of complex enterprise software as well as simpler applications. Need to build a reliable app? Contact the Abto Software team, we are ready to help.


